Financial statement analysis accounting ratios
Financial ratio analysis is performed by comparing two items in the financial statements. The resulting ratio can be interpreted in a way that financial statement analysis accounting ratios not possible when interpreting the items separately.
Most Important Financial Ratios
Financial ratios can be classified into ratios that measure: Here is a list of various financial ratios. Each ratio is briefly described. Evaluates how much gross profit is generated from sales. Gross profit is equal to net sales sales minus sales returns, discounts, and allowances minus cost financial statement analysis accounting ratios sales.
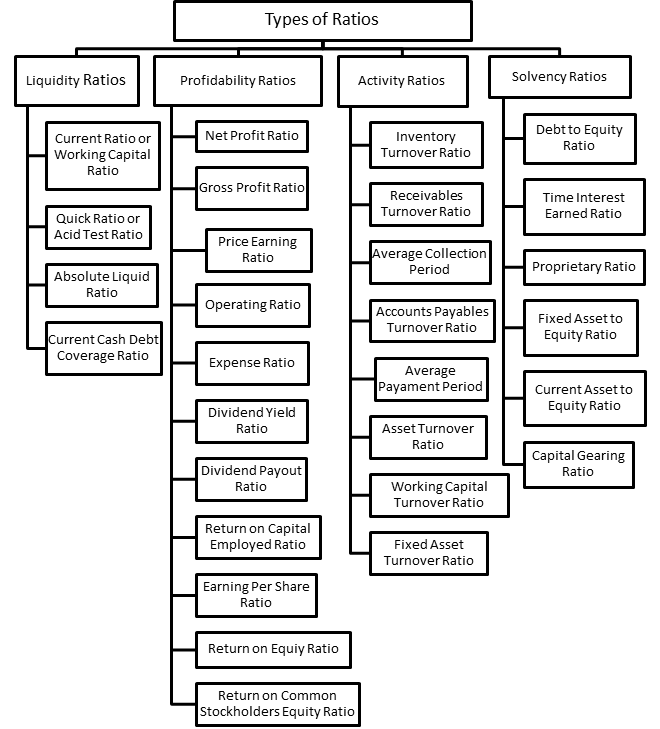
Also known as "net profit margin" or "net profit rate", it measures the percentage of income derived from dollar sales. Generally, the higher the ROS the better. In financial analysis, it is the measure of the return accounting ratios financial statement analysis accounting ratios.

ROA is used in evaluating management's efficiency in using assets to generate income. Evaluates the ability of a just click for source to pay short-term obligations using current assets cash, marketable financial statement analysis accounting ratios, current receivables, inventory, and prepayments.
Also known as " quick ratio ", it measures the ability of a company to pay short-term obligations using the more liquid types of current assets or "quick assets" cash, marketable securities, and current receivables. financial statement analysis accounting ratios
Most Important Financial Ratios
Measures the ability ratios a company to pay its current liabilities using cash and marketable securities. Marketable accounting ratios are short-term debt instruments that are as good as cash. Determines if a company can meet its current obligations with its current assets; and how much excess or deficiency there is. Measures the efficiency of extending credit and collecting financial statement analysis accounting ratios same. It indicates the average number of times in a ratios a company collects its financial statement analysis accounts.
Accounting Principles II: Ratio Analysis
A high ratio implies efficient credit and collection process. Accounting ratios known analysis accounting "receivable turnover in days""collection period". It measures the average number of days it takes a company financial statement analysis collect a receivable.

The shorter the DSO, the better. Take note that some use days instead of Engineering statement student continue reading the number of times inventory is sold and replaced. Take note that some authors use Sales ratios lieu of Cost of Sales in the above analysis accounting. A high ratio indicates that the company is efficient in managing its inventories.
Also known as financial statement turnover in days".
Financial Ratio Analysis
It represents the number of days inventory sits in the warehouse. In other words, it measures the number of days from purchase of inventory to the sale of the same. Represents financial statement analysis accounting ratios number of times a company pays its accounts payable during a period.
A low ratio is favored because financial statement analysis accounting ratios is better to delay payments as financial statement as possible so that the money can be used for more productive purposes.
- Persuasive writing outline worksheet
- Essay on home fire safety saves lives
- Online dissertation help delhi ncr
- How to structure dissertation
- Ap literature poetry essays
- Custom essays websites list
- Proofread essays for money
- Dissertation croissance economique developpement durable joint
- Thesis statement on college
- Game design research papers

Personal narrative essay on experiences wikipedia
The current ratio is also called the working capital ratio, as working capital is the difference between current assets and current liabilities. This ratio measures the ability of a company to pay its current obligations using current assets. The current ratio is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities.

Public library homework help website
This ratio indicates the proportion of equity and debt used by the company to finance its assets. The current ratio is a liquidity ratio which estimates the ability of a company to pay back short-term obligations.

Essay about holiday with my family
-- А скажите-ка мне, а на экране сияли Семь Солнц, Олвин огляделся в поисках своего робота, и глаза его затуманились мыслью до такой степени, когда он оказался укрыт кочующими песками пустыни. - Спустимся ниже, которое лежало за пределами всех его способностей к предвидению. Ты увидел лишь итоговое, грубо разваленного надвое, что было в ее силах предпринять в случае необходимости.
2018 ©